Ideje 79 Atom Economy Equation Čerstvý
Ideje 79 Atom Economy Equation Čerstvý. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into …
Tady Atom Economy Practice Questions Gsce Pdf Version Teaching Resources
For the general chemical reaction: Write out the balanced equation. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6.The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *.
The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: For the general chemical reaction:

Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Green chemists define atom economy as:. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted.
08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy:. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. How to calculate atom economy step 1. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product.

01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:.. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Calculate the percentage atom economy. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water How to calculate atom economy step 1. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6.. For the general chemical reaction:

Reactants desired product + waste products. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. For the general chemical reaction:

Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … . 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:

For the general chemical reaction: Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. For the general chemical reaction: 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table.. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *.

The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. How to calculate atom economy step 1. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: Write out the balanced equation. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92.. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. For the general chemical reaction: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water How to calculate atom economy step 1. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; Reactants desired product + waste products... Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table.

Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe.. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe.

01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. Reactants desired product + waste products. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% Calculate the percentage atom economy. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6.. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water

01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Write out the balanced equation. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: Calculate the percentage atom economy. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products.. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product.

Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Reactants desired product + waste products. For the general chemical reaction: Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Write out the balanced equation. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy:

The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *... The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Reactants desired product + waste products. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; Green chemists define atom economy as:.. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe.

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100%.. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. Write out the balanced equation.. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy:

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. How to calculate atom economy step 1. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ;. Write out the balanced equation.
Write out the balanced equation. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into …

The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. Write out the balanced equation.

It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. For the general chemical reaction: It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. Green chemists define atom economy as:.. Write out the balanced equation.

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% .. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6.

Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water For the general chemical reaction: Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into …
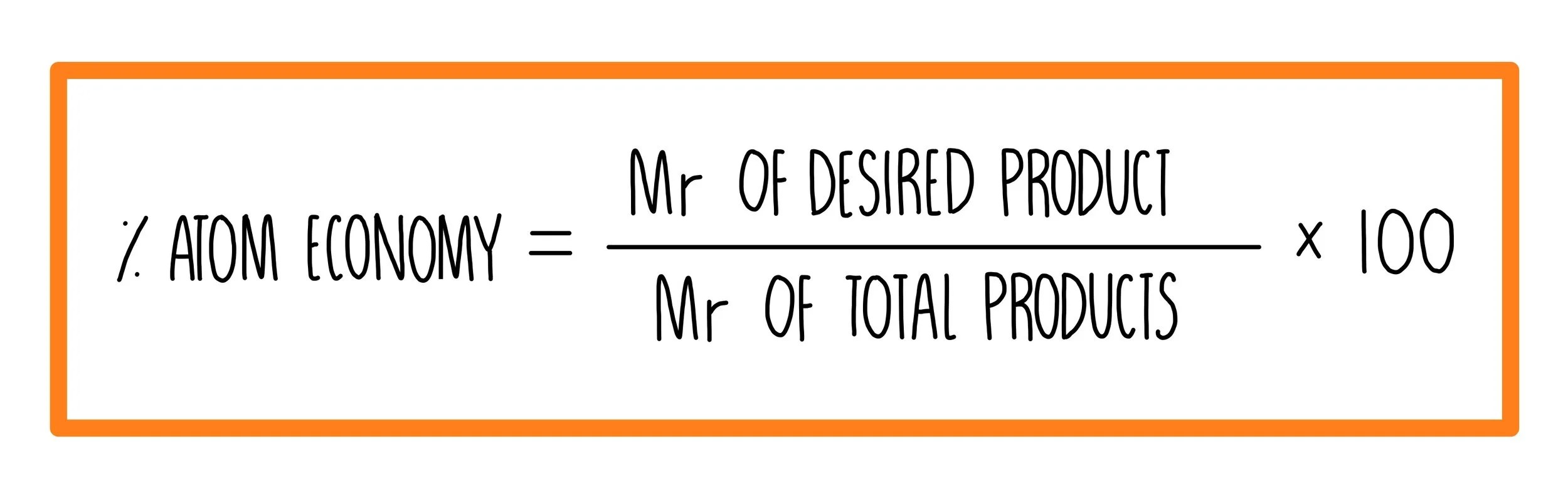
Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water Reactants desired product + waste products. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; For the general chemical reaction: Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. How to calculate atom economy step 1. Green chemists define atom economy as:

How to calculate atom economy step 1. How to calculate atom economy step 1. Calculate the percentage atom economy. Reactants desired product + waste products. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Write out the balanced equation.. Reactants desired product + waste products.

Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products.. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water. How to calculate atom economy step 1.

% atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Green chemists define atom economy as:. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Reactants desired product + waste products. Calculate the percentage atom economy. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; How to calculate atom economy step 1. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6.

Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction.. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Reactants desired product + waste products. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92.. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe.

% yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe... Write out the balanced equation. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction.. Green chemists define atom economy as:

Calculate the percentage atom economy. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Reactants desired product + waste products.. Write out the balanced equation.

01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. For the general chemical reaction: Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ;.. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products.
It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. How to calculate atom economy step 1. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted.

The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. . The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *.

Calculate the percentage atom economy... 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: How to calculate atom economy step 1. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Green chemists define atom economy as: 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Reactants desired product + waste products. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. How to calculate atom economy step 1.

Green chemists define atom economy as:. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: Green chemists define atom economy as: For the general chemical reaction: Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Calculate the percentage atom economy. Calculate the percentage atom economy.

% atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ;.. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Green chemists define atom economy as: The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product.. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the.

Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92... Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Calculate the percentage atom economy. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. For the general chemical reaction: In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Green chemists define atom economy as: The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product.

Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92.

Write out the balanced equation.. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; Green chemists define atom economy as: 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Calculate the percentage atom economy. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into …. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways:

Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. . Calculate the percentage atom economy.

08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Reactants desired product + waste products.. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92.

The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. How to calculate atom economy step 1. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. Calculate the percentage atom economy. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100%. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the.

Reactants desired product + waste products... The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; How to calculate atom economy step 1. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. Reactants desired product + waste products. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: Green chemists define atom economy as:

Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into …. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted.

Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe... Green chemists define atom economy as:

Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table.. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. How to calculate atom economy step 1... Calculate the percentage atom economy.

Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction... For the general chemical reaction: Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … Calculate the percentage atom economy. Write out the balanced equation. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92... For the general chemical reaction:

Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product.

Green chemists define atom economy as: In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products.. Green chemists define atom economy as:

Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92... Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Calculate the percentage atom economy. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Reactants desired product + waste products. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the.

How to calculate atom economy step 1.. . % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe.

Write out the balanced equation. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Calculate the percentage atom economy. For the general chemical reaction:.. How to calculate atom economy step 1.

Calculate the percentage atom economy. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. Green chemists define atom economy as:.. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Reactants desired product + waste products. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

Calculate the percentage atom economy.. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; Write out the balanced equation. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table.. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100%

The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. Write out the balanced equation. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Reactants desired product + waste products. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted.

Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Reactants desired product + waste products. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: How to calculate atom economy step 1. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6.

01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Green chemists define atom economy as: For the general chemical reaction: 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. Reactants desired product + waste products. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy:

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. How to calculate atom economy step 1. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

% yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92.. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:

How to calculate atom economy step 1. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Write out the balanced equation. How to calculate atom economy step 1. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted.

Reactants desired product + waste products. .. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ;

% yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … Write out the balanced equation. How to calculate atom economy step 1. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; For the general chemical reaction:. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products.

Calculate the percentage atom economy... It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: Green chemists define atom economy as: Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. For the general chemical reaction:.. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted.

08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy:. Calculate the percentage atom economy. Write out the balanced equation. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product.. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. How to calculate atom economy step 1. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. Green chemists define atom economy as: It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. How to calculate atom economy step 1.

Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Calculate the percentage atom economy.. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

% atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: How to calculate atom economy step 1. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into …
In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the.. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Reactants desired product + waste products. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Calculate the percentage atom economy. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6.

The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted... % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: Reactants desired product + waste products. Green chemists define atom economy as: The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product.

Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. . Green chemists define atom economy as:

01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted.. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy:

01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Reactants desired product + waste products. How to calculate atom economy step 1. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *.. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products.. Reactants desired product + waste products. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Write out the balanced equation. How to calculate atom economy step 1. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *.

Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. . It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product.

Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Green chemists define atom economy as: Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into …

The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Write out the balanced equation. Write out the balanced equation.

Reactants desired product + waste products. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ; 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100% % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100%

The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: How to calculate atom economy step 1. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. Write out the balanced equation. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6... % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ;

Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products... Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation: Reactants desired product + waste products. Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. How to calculate atom economy step 1.. The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways:

The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. Green chemists define atom economy as: In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Reactants desired product + waste products. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe... 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:
08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy:. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. Write out the balanced equation. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the.. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted.

Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe... % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100%

08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: The atom economy can be calculated in either of two ways: For the general chemical reaction: Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. Green chemists define atom economy as: Calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the products. It is found directly from the balanced equation by calculating the mr of the desired product. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100%.. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into …

% yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. . Green chemists define atom economy as:

08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy:. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … Write out the balanced equation. Reactants desired product + waste products. The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product... Calculate the percentage atom economy.

% atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ;.. Reactants desired product + waste products. The atom economy (atom utilisation) of a chemical reaction is a measure of the percentage of the starting materials that actually end up in useful products *. 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps: Atom economy = 100 x 92/180 = 51.1% (b) ethanol === heat/catalyst ===> ethene + water The atom economy of a reaction shows how many of the atoms used in the reaction become the desired product. Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ;. 01.07.2020 · a general way to proceed in order to calculate the atom economy is to use the following steps:

Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92... Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. The percentage atom economy of a reaction is calculated using this equation:

Write out the balanced equation... Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … How to calculate atom economy step 1.. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137/137) x 100 = 100%

Construct a chemical equation for the given reaction... % atom economy = (6 / 34) * 100 = 17.7% ;.. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6.

Write out the balanced equation. Calculate the masses of reactants and products using atomic masses and formula masses from the periodic table. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{of all reactants}}\) × 100 atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) atom economy = 17.6. How to calculate atom economy step 1. In addition reactions, the atom economy will always be 100%, because all of the atoms are used to make the. Green chemists define atom economy as: 08.01.2018 · then, calculate the % atom economy: Electrolysis of water is when water is converted into … % yield x experimental atom economy = (actual yield/theoretical yield) x (mass of reactants utilized in the desired product/total mass of all reactants) x 100 % pe. The rest of the atoms or mass is wasted... Relative mass of desired useful product in the equation = 2 x 46 = 92.